Defining Biophilic Design in Architecture & Theories Related to Biophilia

Defining Biophilic Design in Architecture & Theories Related to Biophilia
A PART OF THE COMPLETE BIOPHILIC DESIGN FRAMEWORK ADOPTED BY GAUTAM & GAUTAM ASSOCIATES WHILE DESIGNING
Biophilic Architecture Design Series | Ar. Ankur Gautam, Gautam & Gautam Associates | 16 APRIL, 2020
NEED FOR BIOPHILIC DESIGN IN ARCHITECTURE
“The relationship between humankind and nature can be one of respect and love rather than domination…The outcome…can be rich, satisfying, and lastingly successful, but only if both partners are modified by their association so as to become better adapted to each other…With our knowledge and sense of responsibility…we can create new environments that are ecologically sound, aesthetically satisfying, economically rewarding…This process of reciprocal adaptation occurs…through minor changes in the people and their environment, but a more conscious process of design can also take place.”
Planet Earth sustains because of the Yin & Yang that is the mankind and nature. Both of them acts as counterparts, maintaining an equilibrium. We are indeed a miniscule fraction of the planet, recently thrived on. Surrounded by billions of years of researcher-Mother Nature, humans themselves can never be detached from nature as they are said to be made of its 5 Elements: the Earth, the Water, the Air, the Fire and the Wood. After our demise it is the Mother Nature who engulfs us and makes us a part of their never ending ecological processes. Our ancestors have evolved being present in such surroundings, that they have deep reverence and affinity towards Nature, as at that time they were surrounded by nature’s stimulus provided various benefits to the mankind and evolved a mechanised behaviour to positively respond to nature. This conceptualization, termed as Biophilia, is in great demand at present due to the current urbanization, greatly affecting our surroundings and taking us away from nature’s benefits in one way or the other. This change, according to the society, can be bought through application of Biophilia in various aspects of construction of spaces, like Architecture, Interior Designing, etc. Architecture is one such field which has an infinite power to dictate the character and stimuli generation of a space. If bought into Architecture, Biophilic Design can act as bridging the gap between human nature connections and establishing an equilibrium. For this, a framework needs to be generated that would lead to adoption of Biophilic literature, practically, to various aspects of the designing and planning processes.
The term Biophila, coined from two words ‘Bio: nature’ & ‘Philia: love or affinity’ articulates relationship between nature, science and built environment so that we may experience it’s benefits. Biophilic Design is a reflection of human- nature relationship architecturally mend into the built and landscape spaces. The Biophilic concept revolves around a belief that humans hold a biological need for connecting with nature on physical, mental and social levels and their connections affects our personal well being, productivity and societal relationships.
“I can think of no more important way to apply the naturalistic approach to human behaviour than in the design of the places in which we live and work. The evidence is overwhelming that, given a choice, people want to bring the beauty and harmony of nature within site. When possible, they like to blend these qualities into details of their daily existence, because in so doing, they add their own sense of worth and security” (E.O. Wilson)
There have been various attempts by the researchers to describe the Biophilic Design hypothesis of various aspects of the human- nature connections and it’s relation with architecture. Various theories and patterns have been proposed to explain the hypothesis.
This section assists to examine and infer most relevant Biophilic Design Theories and Components as patterns through a common platform, accessible to the designers:
Theories:
- Attention Restoration Theory (ART)
 Stress Reduction Theory (SRT)
Stress Reduction Theory (SRT)- Perceptual Fluency Account (PFA)
- Favourable and unfavourable settings to mental health
- Savannah Hypothesis
- Naturalness and Stress Reduction
- Aesthetic Appeal of Nature
- Fractal Theory
- Prospect and Refuge Theory

- 14 Patterns of Biophilic Design
- Dimensions, Elements, Attributes of Biophilic Design
- Restorative Environment Design (RED)
THEORIES PERTAINING TO BIOPHILIC DESIGN IN ARCHITECTURE
We, as humans have evolved our behaviour mechanism and problem solving tactics mimicking nature, taking lessons from them and in return through our actions and generated stimuli, have shaped our natural environments. It is the presence of natural environment around us which is instrumental in generation of our evolutionary mechanism and ways of getting through the challenges surrounding us. These theories are based on the Biophilic Hypothesis that humans have affiliation and attraction towards nature and natural elements further leading to wellbeing of person as a whole.
The theories, relating to this literature, have been broadly divided to two classifications instrumental in affecting the Human- Nature Relationship:
- Theories on Psycho- Evolutionary and Restorative Preferences
- Nature- Based and Environmental Preferences
Both the preferences are inter-related, providing a common platform for analysis:
BUBBLE DIAGRAM DEPICTING 2 MAJOR PREFERENCES PERTAINING TO THEORY OF BIOPHILIC DESIGN
1. THEORIES ON PSYCHO- EVOLUTIONARY AND RESTORATIVE PREFERENCES
Theories on Psycho-Evolutionary and Restorative preferences have certain links with the Nature- Based and Environmental Preferences. To justify this, the present theories refer to the challenges faced by humans, during evolution and the evolutionary environment which shaped their adaptation mechanism.
Humans, at present, have to undergo constant levels of stress and reduced mental and physical wellbeing as an aspect of evolutionary challenges. This is mainly due to their evolving lifestyles and the environment surrounding them. The conceptualization of the Human-Nature Connection proves instrumental in enhancing physiological, psychological wellbeing and stress reduction in present context. This stimulus can be related back to our ancestors, who also possessed similar stimuli towards Human Nature Connection, in a particular environmental surrounding, facing different evolutionary challenges, as of now.
These evidences concretizes the role of Human- Nature Relationship and provides a framework for generation of a positive and restorative response towards the evolutionary challenges.
Based on these statements, Theories which can be classified under this domain are:
- Attention Restoration Theory (ART)
- Stress Reduction Theory (SRT)
 Perceptual Fluency Account (PFA)
Perceptual Fluency Account (PFA)
A. ATTENTION RESTORATION THEORY
Attention restoration theory is an example of a Restorative Theory synthesized From the Biophilic Hypothesis presented by Dr. Stephen Kaplan, a psychologist, In 1977. According to the hypothesis, human’s response to nature- generated stimuli, through involuntary actions, supported by involuntary attention. This reduces the stress and energy wastage due to cognitive thinking in case of a challenging environment, which deviates a person’s attention.
Thus, this theory, developed by Stephen and Rachael Kaplan (Kaplan and Kaplan, 1989: Kalpan, 1995), explains the restorative quality of nature which restores one’s attention from prolonged tasks that are mentally fatiguing.
From present literature, it is evident that nature, particularly natural elements provides a restorative effect on a person, evident from the ancestral records of nature having a restorative effect. Attention Restoration Theory proposes four elements that promote Cognitive Restoration:
- Fascination
- Being away
- Extent
 Compatibility
Compatibility
FASCINATION:
Fascination refers to the component of ART which is an involuntary action generated due to nature’s beauty, accessed in various dimensions, leaving no room for stress on brain, for cognitive attention to soft and hard fascination:
Hard Fascination: emphasizes on a particular natural element or natural setting, leaving no room for distraction.
Soft Fascination: emphasizes on a variety of natural elements, arranged in a particular pattern, as to engage the person, through a defined path, generating the stimuli for exploration and generation of excitement.

The component emphasizes on the attribute of being physically and psychologically away from a Biophilic element and the restoration quality it generates. It can be through being physically away from the element and reconciling or remembering it, with eyes closed, reducing mental fatigue and energy wastage on cognition or brain functioning.
“This diverts the mind from stresses of work and takes it on natural elements, which doesn’t stresses brain, providing relaxation and restoring brain and neuro-muscular system, restoring a person’s attention” (Tatiana Abaurre Alencar,2010: biophilic design framework: Structuring the relationship between exposure to nature and health benefits,p.64)

It emphasizes on the extent of natural surroundings those are efficient to engage a person through a continuous series of attention generating elements, further generating fascination.
If the extent is at a micro level, say potted plants, the attention restoration would be minimal, in comparison to field of flowers or forest, providing ample extent.

Compatibility component emphasizes that the natural environment and elements provided and the human inclination towards it must be compatible and complementary. That is, the human inclination shall be fulfilled without much struggle or effort. Thus, the experiences those takes place within this component ought to have a high degree of compatibility.
B. STRESS REDUCTION THEORY (SRT)

The stress recovery theory devised by Roger Ulrich in 1983, in his article
“Aesthetic and affective response to natural environments”, concerns recovery from psychological stresses. According to this theory, stress is described as a process of generation of human stimuli in response of events, environmental features or situations that are considered as a threat to persons well being. This further generates negative emotions.
Based on work of Zojonc(1980), Roger Ulrich argues initial response of a person towards an unfamiliar or unknown environment is one of a dislike or disinterest, until specific environmental features are addressed like:
Presence of vegetation: complexity: symmetries: textures: views : vistas and absence of elements, leading to generation of threat.
These features are said to reduce negative emotions and disliking and arouses attachment or attraction, providing a restorative experience. Roots of these features lies in the evolutionary adaptation and the environmental conditions present during that time. Thus, nature based features may reduce stress, but not artificial or non- natural features like glass, aluminum, etc.

C. PERCEPTUAL FLUENCY ACCOUNT (PFA)
PFA acts as an intersection of ART and SRT Theories. The synthesis of this theory dictates that human brain can more frequently and fluently comprehend and generate stimuli to a natural setting in a structured manner, than an urban setting, dominating on the built environments. Thus, fluent encounters, reduces stress on cognition of brain, restoring attention and ultimately, reducing stress.
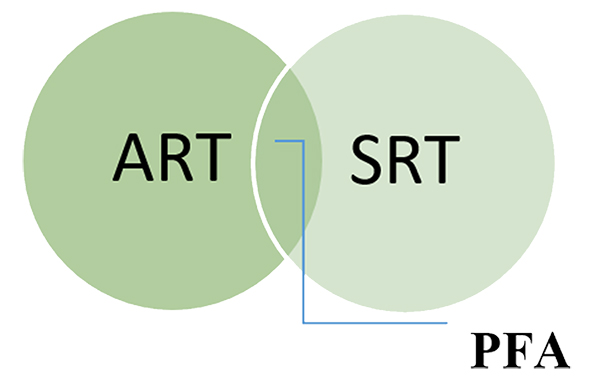
The Bubble diagram showing intersection of Attention Restoration Theory and Stress Reduction Theory forming an intersection at PFA.
2. THEORIES ON NATURE-BASED AND ENVIRONMENTAL PREFERENCES
Theories on nature-based and environmental preferences are based on the concept that humans have affiliation towards nature, evident from the evolutionary adaptation of the evolutionary adaptation of the ancestors in a natural setting and surroundings.
According to the present literature, present theories pertaining to this domain, can be divided into four preferences:
- Savannah Hypothesis
- Prospect and Refuge Theory
- Fractal Theory
 Aesthetic Appeal of Natural Content
Aesthetic Appeal of Natural Content
A. SAVANNAH HYPOSTHESIS
Savannah Hypothesis, introduced by Ecologist Gordon Orions in 1980, emphasizes on the “Environment Selective Theory”. This theory specifies that humans prefers Landscape features to have elements from the African Savannah.
As Orions argued that due to long history of survival of humans in the Savannah Environment and evolutionary adaptation taking place in these environments, generated psychological linkages with the Savannah like landscapes.
Thus, a person would intrinsically prefer a Savannah like landscape than present cityscape, that would lead to well being of a person. The features of Savannah-
“ like landscapes include high diversity of flowers; animal lives; scattered cluster of trees; topographic changes; scattered water bodies and multiple long- distances view corridors for surveillance for predators and a bright obstruction free sky. ”
B. PROSPECT-REFUGE THEORY

For geographer Jay Appleton(1975) , the ability of a person to view a space, without being seen by any other person, is described as the main motivation of this theory, to view a space is “Prospect” and not being seen by others is “Refuge”.
The existence of this theory can be linked to our ancestors for whom shelter has been a vital element, be it any form, providing a refuge from outside world and at the same time surveilling areas around from enclosed space, that is Prospect.
Prospect and Refuge can’t exist singularly at any place as both are at equilibrium, where prospect can be divided to two parts:
Direct: emphasizing on views and vistas, directly visible from a point
Indirect: or deflected vistas, in which vistas change after every point of movement of the viewer.
And Refuge being small and dark, where a person feels secured.
C. FRACTAL THEORY

Fractal theory is led by the ideology that the fractal geometries, present in nature, if mimicked in various components of the built environment, can promote stress- reduction and well being, visually. This concept, generated by Mandelbrot in 1977, suggests that fractal components enhances well being rather than non- fractal components and can be incorporated into various elements of Built- spaces like the staircase design symbolizing fractals and so on.
D. AESTHETIC APPEAL OF NATURAL CONTENTS

It is generally observed that the natural elements like indoor plants when incorporated into interior design, increases the aesthetic appeal of the space, re-establishing the human- nature connection.
The present proposed theories describes aptly and justifies the Biophilic Hypothesis, where the two preferences co-exists in harmony and are pivotal in being a major component of the Biophilic framework. Hence, the present theories are adopted in the process of Framework design for adaptation of Biophilia in architectural design, without much modifications and are present in a singular structural system:
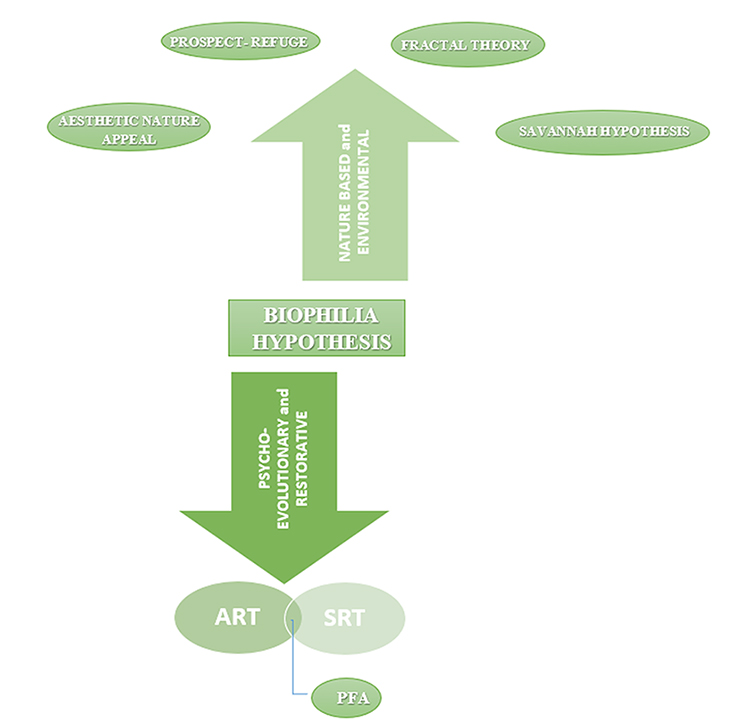
THE DIAGRAM ILLUSTRATING & CONCLUDING THE PRESENT LITERATURE & EXTENT OF BIOPHILIA HYPOTHESIS IN ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN & EXISTING THEORIES PERTAINING TO THE SAME
GAUTAM & GAUTAM ASSOCIATES following a sustainable design practise, focuses on biophilic theories & design guidelines to design a project from inception to completion. these theories are used as a part of a complete biophilic design framework & action plan, adopted by Gautam & Gautam Associates for each project.
FOR DETAILED INSIGHT TO OUR PROJECTS, VISIT: https://gngindia.com
Developed by Abacus Desk

